Hogyan érheti el a központi vénás katéterkészlet orvosi célokat a különféle alkatrészek szinergiáján keresztül?
A készlet alapkomponenseinek elemzése
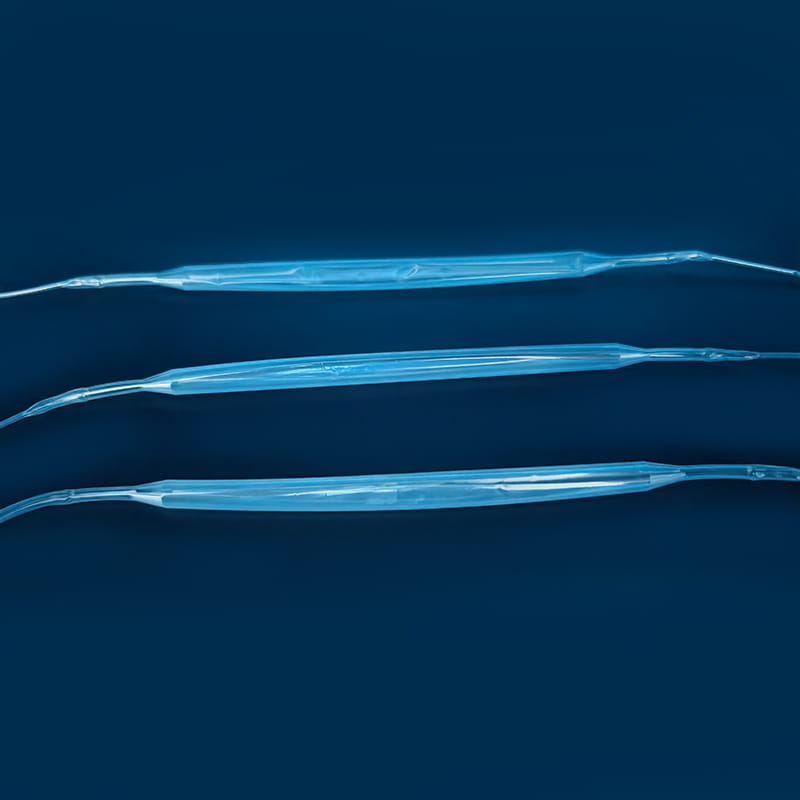
A központi vénás katéterkészlet Különféle kulcsfontosságú elemeket tartalmaz, amelyek mindegyike egyedi és pótolhatatlan szerepet játszik a teljes orvosi működési folyamatban. Az első a központi vénás katéter, amely a készlet alapvető alkotóeleme, és a csatorna, amely a központi vénát összeköti a testen és a test belsejében. Anyagát általában orvosi minőségű poliuretánból vagy szilikonból készítik. Az ilyen anyagok jó biokompatibilitást mutatnak, és hatékonyan csökkenthetik az idegen testek elutasítását, és csökkenthetik a szövődmények, például a fertőzés kockázatát. Különböző típusú központi vénás katétereknek megvannak a saját tulajdonságai a szerkezetben és a funkcióban. Az egy lumen katéterek alkalmasak az egyszemélyes kezelési igényekre, míg a kettős lumen vagy több lumen katéterek egyidejűleg különféle orvosi műveleteket végezhetnek, mint például az infúzió, a vérgyűjtés és a gyógyszerügynökség, amely jelentősen javítja az orvosi műveletek hatékonyságát és kényelmét. A tervezés szempontjából néhány katéter felületet speciális bevonatokkal kezelnek, hogy tovább javítsák az anti-trombotikus tulajdonságokat; Néhányan mérlegekkel vannak megjelölve, hogy megkönnyítsék az orvosi személyzetet, hogy pontosan megragadják a beillesztési mélységet.
A cannula plays a pioneering role in the central venous catheter kit. When performing a central venous catheter insertion operation, the cannula is first used for percutaneous puncture into the vein. Its needle tip adopts a bevel cutting process. This design is sharp and precise, and can quickly and accurately penetrate the skin and vein wall with minimal resistance, opening a channel for the entry of subsequent components. The needle core and outer sleeve of the cannula needle are closely matched. When the cannula needle successfully enters the vein, the inner needle core is removed through a special separation mechanism, and the outer sleeve with a certain hardness and flexibility will remain in the vein as a guide channel for subsequent guide wires and other components to enter. To ensure the accuracy of puncture, some cannula needles are also equipped with ultrasound guidance adapters, which can be used with ultrasound equipment to observe the puncture path and blood vessel status in real time.
A guidewire is a key tool for precise positioning and guidance in the central venous catheter kit. After the cannula needle establishes the initial channel, the guidewire will be sent into the vein through the cannula. The outer layer of the guidewire is usually woven from medical-grade stainless steel wire, and the inner layer is a nickel-titanium alloy core. This structure gives the guidewire good flexibility and maneuverability. Doctors can use the J-shaped or straight head design of the guidewire tip to flexibly turn and guide it in the blood vessel through in vitro operation, and accurately send it to the target position. Some high-end guidewires also have a hydrophilic coating, which becomes lubricated after contact with blood, further reducing friction damage to the inner wall of the blood vessel. The existence of the guidewire makes the insertion path of the central venous catheter clearer and more controllable, laying a solid foundation for the smooth insertion of the subsequent catheter.
A role of the dilator in the central venous catheter kit should not be ignored. Since the diameter of the vein is relatively thin, and the central venous catheter needs to be smoothly inserted, it is necessary to properly dilate the vein. The dilator usually adopts a conical or cylindrical design, and the material is mostly medical-grade polyethylene. It can enter the vein along the guidewire and expand the channel of the venous puncture site by gradually expanding. During the expansion process, the smooth surface treatment and gradual caliber design of the dilator can reduce damage to the venous tissue while ensuring effective expansion. For special patients, such as those with thin blood vessel walls or sclerosis, there are also special controllable dilators available, and doctors can accurately adjust the expansion strength and range according to actual conditions.
A peelable sheath is an important part of the central venous catheter kit to ensure the safe insertion of the catheter. After the dilator completes the dilation of the vein, the peelable sheath will be sent into the vein along the guidewire and dilator. The peelable sheath consists of two symmetrical half sheaths connected by a special locking structure in the middle. When the peelable sheath reaches the appropriate position, the central venous catheter will be inserted into the vein through the sheath. At this time, the medical staff will separate the peelable sheath from the middle lock and remove it from the body through a specific operation technique, while the central venous catheter will be left in the vein. This unique design not only ensures the smooth catheter insertion process, but also avoids unnecessary damage to the vein and catheter. To prevent accidental scratches on the surrounding tissue when the sheath is peeled off, the edge of the sheath is specially rounded and blunted.
A fixing device plays a role in stabilizing and fixing the catheter in the central venous catheter kit. In order to ensure that the central venous catheter can maintain a stable position in the patient's body for a long time without displacement or falling off, fixing devices such as sutures, sterile dressings or special catheter fixers will be used to fix the catheter to the patient's skin. The suture fixation method is suitable for patients with long-term catheterization. The catheter is fixed to the skin tissue through delicate suturing operations; the sterile dressing is breathable, waterproof and antibacterial, and can effectively protect the puncture site; the dedicated catheter fixator is made of medical-grade silicone or polymer materials, and can be personalized according to the patient's skin morphology and catheter model through an adjustable buckle design. Appropriate fixation can not only ensure the normal function of the catheter, but also reduce the discomfort and potential risks caused to the patient by the movement of the catheter.
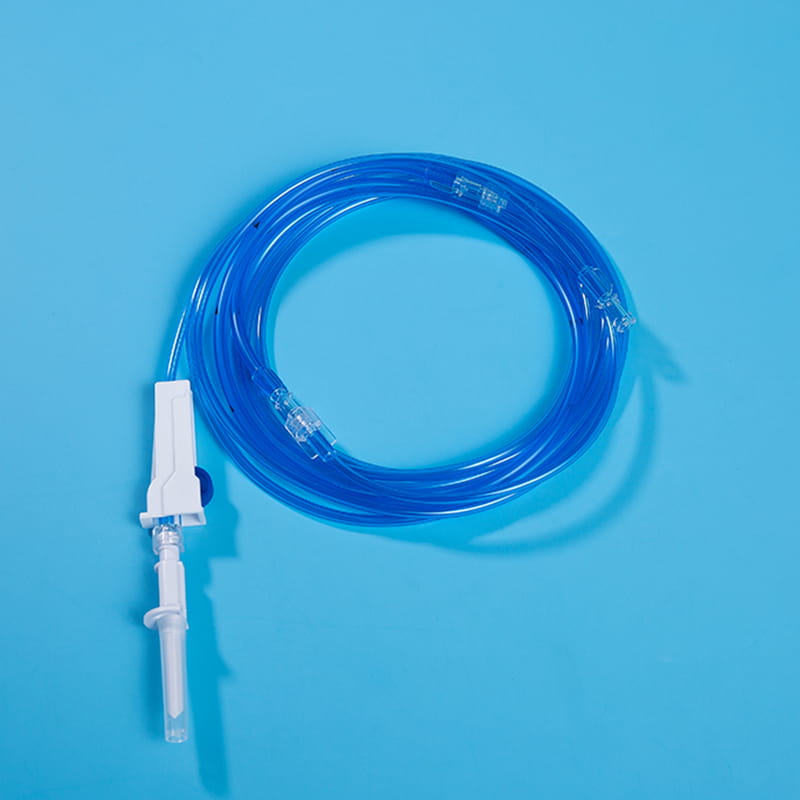
A interface for external connection is the bridge between the central venous catheter and external medical equipment. Through these interfaces, the central venous catheter can be connected to infusion sets, syringes and other equipment to achieve various medical operations such as infusion, drug administration, and blood collection. The design of these interfaces has good sealing and compatibility, and common ones include Luer connectors and needleless infusion connectors. The Luer connector is connected by threads to ensure a tight connection without leakage; the needleless infusion connector adopts a diaphragm design, which can complete the infusion operation without acupuncture, reducing the risk of infection. At the same time, some interfaces also have anti-backflow function to prevent blood from reflux and blocking the catheter, and support multiple devices to be connected at the same time to meet complex clinical needs.
A klinikai alkalmazási forgatókönyvek széles skálája
A tényleges orvosi alkalmazásokban a központi vénás katéterkészletek felhasználási forgatókönyvei nagyon szélesek. Az intenzív ellátás területén olyan kritikus állapotú betegek számára, akiknek nagy mennyiségű infúzióra és gyakori gyógyszerre van szükségük, a központi vénás katéterek gyors és stabil infúziós csatornát biztosíthatnak a betegek és a gyógyszerek igényeinek kielégítésére. Például szeptikus sokkban szenvedő betegeket véve a mentési folyamat során nagy mennyiségű kristályloid folyadékot, kolloid folyadékot és vazoaktív gyógyszert kell kiegészíteni rövid idő alatt. A központi vénás katéter biztosítja, hogy ezek a folyadékok és gyógyszerek gyorsan belépjenek a vérkeringésbe, és gyorsan kijavítsák a sokk állapotát. Ugyanakkor a hemodinamikai megfigyelés a központi vénás katéteren keresztül is elvégezhető. Az orvos összekapcsolja a nyomásérzékelőt a katéter interfészével, hogy olyan paraméterekkel, mint a központi vénás nyomás és a tüdő artériás ék nyomás valós időben kapjon, ami segít az orvosoknak a beteg szívfunkciójának és a vérkeringés állapotának megértésében, és fontos alapot nyújt a pontos kezelési tervek kidolgozásához.
A daganatos kezelés során számos kemoterápiás gyógyszer nagyon irritálja az ereket, és a perifériás vénákon keresztül történő beadás szövődményeket okozhat, például flebitis. A központi vénás katéterkészlet egy katétert helyezhet a központi vénába, lehetővé téve a kemoterápiás gyógyszerek számára, hogy közvetlenül belépjenek a nagy erekbe és gyorsan hígítsák, ezáltal csökkentve az erek irritációját, csökkentve a szövődmények valószínűségét, és javítva a betegek kezelési toleranciáját és megfelelését. Például azok a mellrákos betegek, akik nagyon irritáló kemoterápiás gyógyszereket, például a doxorubicint kapnak, felhasználhatják a központi vénás katétereket, hogy hatékonyan kerüljék a súlyos következményeket, például a bőr nekrózisát és a gyógyszer -extravazáció által okozott szövetfekélyt. Ugyanakkor a hosszú távú és többszörös kemoterápiára szoruló betegek számára a központi vénás katéterek csökkentik az ismételt lyukasztások fájdalmát és javítják a kezelés folytonosságát.
Ezenkívül a tápláléktámogatási terápiában a központi vénás katéterek felhasználhatók teljes parenterális táplálkozási támogatásra azoknak a betegeknek, akik nem tudnak elegendő táplálkozást a gyomor-bél traktuson keresztül, például hosszú távú kómában és súlyos égési sérülésekben. A magas koncentrációjú, magas kalóriatartalmú tápanyag-oldat megadása a központi vénán kielégítheti a beteg testének tápanyagok igényeit és elősegítheti a beteg gyógyulását. Példaként figyelembe véve a kiterjedt égési sérüléseket, a gyomor -bélrendszeri funkciókat a trauma miatt elnyomják, és nem képesek normálisan emésztni és felszívni az ételeket. Ebben az időben az aminosavakat, a zsír-emulziót, a glükózt és más összetevőket tartalmazó, a központi vénás katétert tartalmazó aminosavakat tartalmazó összes tápanyag-oldatot a beteg nitrogén-egyensúlyának fenntartása, a test által megkövetelt energia feltöltése és a sebgyógyulás felgyorsítása érdekében adjuk meg. Ugyanakkor az orvosi személyzet a központi vénás katéteren keresztül figyelheti a beteg elektrolitjait, vércukorszintjét és egyéb mutatóit, és időben beállíthatja a táplálkozási támogatási tervet.
Szigorú és szabványosított működési eljárások
A operating procedures of the central venous catheter kit need to strictly follow the specifications and standards. Before the operation, the doctor needs to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition, including the patient's age, weight, underlying diseases, coagulation function, etc., and select the appropriate puncture site and central venous catheter type. Common puncture sites include the internal jugular vein, subclavian vein and femoral vein. Different sites have their own advantages and disadvantages, and they need to be carefully selected according to the specific situation of the patient. At the same time, detailed explanations and communication should be given to the patient, and the patient should be informed of the operation process, possible risks and key points of cooperation to obtain the patient's cooperation. During the operation, the principle of aseptic operation must be strictly followed. The puncture site must be disinfected with iodine more than three times, and the diameter of the disinfection range must not be less than 15 cm. A large sterile sheet must be laid to ensure that the entire operation is carried out in a sterile environment. Then follow the steps of trocar puncture, guide wire insertion, dilation with a dilator, insertion of a removable sheath, insertion of a central venous catheter, fixation of the catheter, and connection of an external interface. Taking internal jugular vein puncture as an example, under ultrasound guidance, after determining the puncture point, the trocar is inserted at an angle of 30-45 degrees. After seeing the blood return, it is confirmed that it is in the vein, and then the subsequent components are inserted according to the process. After the operation is completed, the patient needs to be closely observed and cared for, and the patient must be monitored for complications and treated in a timely manner. This includes observing whether the puncture site is red, swollen, or exuded, and changing the dressing regularly; monitoring the patient's body temperature, blood routine, and other indicators to determine whether an infection has occurred; evaluating the function of the catheter to ensure smooth infusion, blood collection, and other operations.
Kihívások és kockázatok
Noha a központi vénás katéterkészletek fontos szerepet játszanak az orvosi területen, felhasználás során néhány kihívással és kockázattal szembesülnek. A fertőzés a központi vénás katéterek egyik leggyakoribb szövődménye. Mivel a katéter hosszú ideig a testben marad, a baktériumok és más mikroorganizmusok behatolása könnyű, és helyi fertőzést vagy szisztémás fertőzést okozhat. A baktériumok elsősorban a testbe a bőr kolonizációjával lépnek be a lyukasztási helyen, a katéter csatlakozójának szennyeződése és az infúziós rendszer szennyeződése révén. A trombózis szintén olyan probléma, amelyet nem lehet figyelmen kívül hagyni. A katéter stimulálhatja az érrendszer vaszkuláris endotéliumát, ami változásokat okozhat a vér koagulációjában, ezáltal trombust képezve. Amint a trombus leesik, súlyos szövődményeket okozhat, például tüdőembólia. Ezenkívül olyan problémák, mint a katéter elzáródása és elmozdulása, befolyásolhatják a központi vénás katéter normál felhasználási és kezelési hatását. A katéter elzáródását a gyógyszer lerakódása, a vér koagulációja stb.; A katéter elmozdulása olyan tényezőkhöz kapcsolódhat, mint a nem megfelelő beteg aktivitás és a laza rögzítés.
For more information, please call us at +86-18913710126 or email us at .
A vaszkuláris intervenciós eljárások szerves részét képezik a modern kardiovaszkuláris gyógyászat...
Bevezetés Egylumenes endobronchiális cső A légzésterápia kritikus öss...
A modern gyógyászatban az orvosi katéterek nélkülözhetetlen eszközök a kezelések és diagnosztikai...
Az egészségügyi iparban nem lehet túlbecsülni az orvostechnikai eszközök megfelelő anyagainak kiv...
A precíziós orvoslás korszakában egy kis cső gyakran hordozza az életmentő feladatok súlyát. Az i...
A modern egészségügyben a precíz folyadékkezelés kulcsfontosságú a betegbiztonság és a kezelés ha...